VOLTMETER
Introduction
A voltmeter is also known as voltage meter. It is an instrument used for measuring the potential difference, or voltage between two points in an electrical or electronic circuit. We know that the unit of potential difference is volts. It works on the principal that the torque is generated by the current which induces because of measured voltage and torque deflects the pointer of the instrument.Some voltmeter are intended for use in DC circuit, others are designed for alternating current AC circuits. The voltmeter is always connected in parallel with the circuit , because voltmeter is constructed in such a way that their internal resistance always remain high .
If voltmeter connects in series with circuit ,it minimises the current which flows because of the measured voltage. Thus, disturb the reading of voltmeter that's why, voltmeter always connected in parallel with circuit so that the same voltage drop occurs across it. The high resistance of voltmeter combines with the impedance of the element across which it is connected. And the overall impedance of the system is equal to impedance that the element had . Thus, no obstruction occurs in the circuit because of voltmeter, and the meter gives the correct reading.
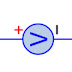
Symbol of Voltmeter
A voltmeter in a circuit diagram is represented by the letter V inside a circle with a wavy line along with the two terminal.
Types of Voltmeter
The voltmeter is classified into three ways . The classification of the voltmeter is shown in fig:
Working principle of Voltmeter -
It's working is based on the principle of Ohm's law , states that `Voltage across a resistance is directly proportional to current passing through it. Any basic meter has a potential difference across it's terminals when a full - scale current flows through it . A voltmeter is always connected in parallel to component in a circuit for which the voltage is to be measured .
A DC voltmeter has polarity signs on it. Therefore one has to connect the plus(+) terminal of the voltmeter to the higher point of potential and the minus (-) terminal to the lower point of potential in order to obtain meter deflection .
In an AC voltmeter there is no polarity signs on it and can be connected anyways. However, in this case also , the Voltmeter is still connected in parallel to the component for which the voltage is measured.
If it is connected in parallel than the load impedance comes parallel with the high resistance of voltmeter and hence the combination will give almost the same impedance that the load had. Also in parallel circuit we know that the voltage is same so the voltage between the voltmeter and the load is almost same and hence, voltmeter measures the voltages.
For an ideal voltmeter , we have the resistance is to be infinity and hence the current drawn to be zero so there will be no power loss in the instrument. But this is not achievable practically as we cannot have a material which has infinite resistance.
Advantages of Voltmeter
There are following advantages of electronic voltmeter:
- There is no circuit loading on voltage measurement.
- They have high sensitivity due to high input impedance.
- They have wide range of frequency response.
- They have burnout resistance meter circuit.
They are accurate and are dependable .
Application of Voltmeter
It has many applications such as:
- Voltmeter provide a way to safely measure the voltage or the potential difference between two points.
- Voltmeter is used to define the battery is charged or not.










Nice explanation
ReplyDeleteItne type toh mereko bhi nahi pata the voltmeter ke 😝
ReplyDeleteThank you for introducing them