Capacitor
Introduction
A capacitor is a two terminal electrical component. Along with resistors and inductors, they are one of the most fundamental passive components we use, a capacitor is a device that stores electrical energy in an electric field . It holds the electric charge when we apply a voltage across it, and it gives up the stored charge to the circuit as when required.
The capacitor consists of two parallel metallic plates separated by a dielectric material. We can say that, it is like a small rechargeable battery . The conductive metal plates of a capacitor can be either square, circular or rectangular, or they can be of a cylindrical or spherical shape with the general shape, size and construction of a parallel plate capacitor depending on its Voltage rating .
When we used DC circuit, a capacitor charges up to its supply voltage but blocks the flow of current through it because the dielectric of a capacitor is non- conductive and basically an insulator , and when a capacitor is connected to an AC circuit the flow of current appears to pass straight through the capacitor with little or no resistance.
There are many different kinds of capacitor available from very small capacitor beads used in resonance circuits to large power factor correction capacitors but they all do the same thing they store charge.
A capacitor is a two terminal electrical component. Along with resistors and inductors, they are one of the most fundamental passive components we use, a capacitor is a device that stores electrical energy in an electric field . It holds the electric charge when we apply a voltage across it, and it gives up the stored charge to the circuit as when required.
The capacitor consists of two parallel metallic plates separated by a dielectric material. We can say that, it is like a small rechargeable battery . The conductive metal plates of a capacitor can be either square, circular or rectangular, or they can be of a cylindrical or spherical shape with the general shape, size and construction of a parallel plate capacitor depending on its Voltage rating .
When we used DC circuit, a capacitor charges up to its supply voltage but blocks the flow of current through it because the dielectric of a capacitor is non- conductive and basically an insulator , and when a capacitor is connected to an AC circuit the flow of current appears to pass straight through the capacitor with little or no resistance.
There are many different kinds of capacitor available from very small capacitor beads used in resonance circuits to large power factor correction capacitors but they all do the same thing they store charge.
History
In October 1745, Ewald George Von Kleist (1700-1748) of Pomeranian invented the first recorded capacitor: a glass jar containing a conducting fluid , such as Mercury, which he held in his hand and an iron nail or wire inserted into the fluid. He found that device could retain a charge after he electrified it with his frictional machine. He claimed to be able to ignite spirits with the nail.
He communicated his discovery to a group of german scientists in late 1745 and the news made its way to Leyden university in the Netherlands, but in a confused form. In 1746 peter van Musschenbroek and his student Andreas Cunaeus at Leyden university succeeded in doing the same experiment but with water.
Musschenbroek then informed the wider french scientific community of the experiment. It's considered that Von Kleist and Musschenbroek independently discovered it. At the earlier , the unit of capacitor is known as jar.
In 1776 Allesendro Volta , working with different methods to measure electrical potential (voltage,V) and charge (Q) discovered that for a given object V and Q are proportional, i.e law of capacitance, though it was not called that at the time. It was for this work that the unit Volt was named after him.
In the 1830s Michael Faraday did experiments which determined that the material in between the capacitor's plates had an effect on the quantity of charge on the capacitor's plates. He did these experiments with spherical capacitors, basically two concentric metal spheres in btw which he could have air , glass, wax materials. Using a coulomb's torsion balance , he effectively measured charge on the capacitor when the gap between the spheres was filled with air. Keeping the potential difference constant he then measured the charge when the gap was filled with other materials .he found that the charge was greater with the other materials than it was with air. He called it the specific inductive capacity and it was for this work that the unit for capacitance is called the farad.
Faraday made major contribution to capacitor technology, including the concept of dielectric constant as well as the invention of the first practical fixed and variable capacitors. His contribution to capacitor technology are recognised in the unit for capacitance .
Symbol
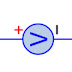
A capacitor consists of two plates that are parallel to each other. In the same way, the symbol represents the plates along with the separation. Even two end terminals that are used in the circuit connections can be shown in the symbol. These capacitors are available in various symbols and types.
Unit.
The standard unit of capacitance is called the farad, which is abbreviated F.
Capacitors in series and parallel:
Capacitors are connected together in parallel when both of its terminals are connected to each terminal of another capacitor. When capacitors are connected in parallel, the total capacitance is the sum of the individual capacitors’ capacitances.The voltage ( Vc ) connected across all the capacitors that are connected in parallel is the SAME.
If two or more capacitors are connected in parallel, the overall effect is that of a single equivalent capacitor having the sum total of the plate areas of the individual capacitorsThen, Capacitors in Parallel have a “common voltage” supply across them giving:
The total capacitance is more than any one of the individual capacitors’ capacitances. The formula of parallel capacitors is
In 1776 Allesendro Volta , working with different methods to measure electrical potential (voltage,V) and charge (Q) discovered that for a given object V and Q are proportional, i.e law of capacitance, though it was not called that at the time. It was for this work that the unit Volt was named after him.
In the 1830s Michael Faraday did experiments which determined that the material in between the capacitor's plates had an effect on the quantity of charge on the capacitor's plates. He did these experiments with spherical capacitors, basically two concentric metal spheres in btw which he could have air , glass, wax materials. Using a coulomb's torsion balance , he effectively measured charge on the capacitor when the gap between the spheres was filled with air. Keeping the potential difference constant he then measured the charge when the gap was filled with other materials .he found that the charge was greater with the other materials than it was with air. He called it the specific inductive capacity and it was for this work that the unit for capacitance is called the farad.
Faraday made major contribution to capacitor technology, including the concept of dielectric constant as well as the invention of the first practical fixed and variable capacitors. His contribution to capacitor technology are recognised in the unit for capacitance .
Units and symbol
A capacitor consists of two plates that are parallel to each other. In the same way, the symbol represents the plates along with the separation. Even two end terminals that are used in the circuit connections can be shown in the symbol. These capacitors are available in various symbols and types.
Unit.
The standard unit of capacitance is called the farad, which is abbreviated F.
| Prefix Name. | Weight | Equivalent Farard | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Picofarad (pF) | 10-12 | 0.000000000001 F | |
| Nanofarad(nF) | 10-9 | 0.000000001 F | |
| Microfarad | 10-6 | 0.000001 F | |
| Milifarad(mF) | 10-3 | 0.001 F | |
| Kilofarad(kF) | 103 | 1000Fp |
Capacitors in series and parallel:
Parallel capacitors.
If two or more capacitors are connected in parallel, the overall effect is that of a single equivalent capacitor having the sum total of the plate areas of the individual capacitorsThen, Capacitors in Parallel have a “common voltage” supply across them giving:
VC1 = VC2 = VC3 = VAB = 12V
In the following circuit the capacitors, C1, C2 and C3 are all connected together in a parallel branch between points A and B
The total capacitance is more than any one of the individual capacitors’ capacitances. The formula of parallel capacitors is
Capacitors in series
Capacitors are connected together in series when they are chained together in a single line.When capacitors are connected in series, the total capacitance is less than any one of the series capacitors’ individual capacitances.For series connected capacitors, the charging current ( iC ) flowing through the capacitors is THE SAME for all capacitors as it only has one path to follow. Then, Capacitors in Series all have the same current flowing through them as iT = i1 = i2 = i3 etc. Therefore each capacitor will store the same amount of electrical charge, Q on its plates regardless of its capacitance. This is because the charge stored by a plate of any one capacitor must have come from the plate of its adjacent capacitor. Therefore, capacitors connected together in series must have the same charge.
QT = Q1 = Q2 = Q3 ….etc
Consider the following circuit in which the three capacitors, C1, C2 and C3 are all connected together in a series branch across a supply voltage between points A and B.
The total capacitance is less than any one of the individual capacitors’ capacitances. The formula for calculating the series total capacitance
Types of capacitor:
Fixed capacitor- A fixed capacitor is one where the conducting surfaces are not adjustable. Fixed capacitor is a type of capacitor which provide fixed amount of capacitance. A fixed capacitor is classified according to the type of material used as it's dielectric , such as paper, oil , mica etc. There are mainly five types of fixed capacitor are as follows-
- Paper capacitor
- Plastic capacitor
- Ceramic capacitor
- Mica capacitor
Electrolytic capacitor




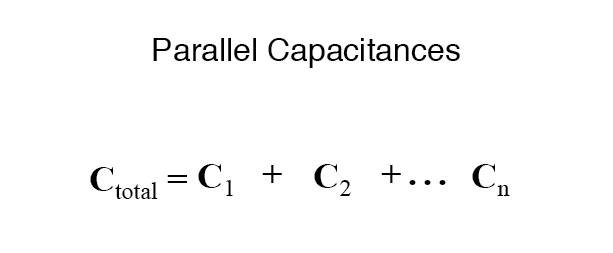











No comments: