LDR (LIGHT DEPENDENT RESISTOR)
INTRODUCTION

A Light Dependent Resistor (also known as a photoresistor or LDR) is a device whose resistivity is a function of the incident electromagnetic radiation. Hence, they are light-sensitive devices. They are also called as photoconductors, photoconductive cells or simply photocells.
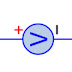
They are made up of semiconductor materials that have high resistance. There are many different symbols used to indicate a photoresistor or LDR, one of the most commonly used symbol is shown in the figure . The arrow indicates light falling on it.
Working Principle of Photoresistor (LDR)
So how exactly does a photoresistor (i.e. a light dependent resistor or LDR) work? Photoresistors work based off of the principle of photoconductivity. Photoconductivity is an optical phenomenon in which the material’s conductivity is increased when light is absorbed by the material.
When light falls i.e. when the photons fall on the device, the electrons in the valence band of the semiconductor material are excited to the conduction band. These photons in the incident light should have energy greater than the bandgap of the semiconductor material to make the electrons jump from the valence band to the conduction band.
Hence when light having enough energy strikes on the device, more and more electrons are excited to the conduction band which results in a large number of charge carriers. The result of this process is more and more current starts flowing through the device when the circuit is closed and hence it is said that the resistance of the device has been decreased. This is the most common working principle of LDR.
Characteristics of Photoresistor (LDR)
Photoresistor LDR’s are light-dependent devices whose resistance is decreased when light falls on them and that is increased in the dark. When a light dependent resistor is kept in dark, its resistance is very high. This resistance is called as dark resistance. It can be as high as 1012 Ω and if the device is allowed to absorb light its resistance will be decreased drastically. If a constant voltage is applied to it and the intensity of light is increased the current starts increasing. The figure below shows the resistance vs. illumination curve for a particular LDR.

Photocells or LDR’s are nonlinear devices. Their sensitivity varies with the wavelength of light incident on them. Some photocells might not at all response to a certain range of wavelengths. Based on the material used different cells have different spectral response curves.
When light is incident on a photocell it usually takes about 8 to 12 ms for the change in resistance to take place, while it takes one or more seconds for the resistance to rise back again to its initial value after removal of light. This phenomenon is called a resistance recovery rate. This property is used in audio compressors.
Also, LDR’s are less sensitive than photodiodes and phototransistors. (A photo diode and a photocell (LDR) are not the same, a photo-diode is a pn junction semiconductor device that converts light to electricity, whereas a photocell is a passive device, there is no pn junction in this nor it “converts” light to electricity).
Types of Light Dependent Resistors (LDRs or Photoresistors)
Photoresistors (LDRs) can be categorized into two types depending on the materials used to construct them. The two types of photoresistors include:
- Intrinsic photoresistors (Undoped semiconductor): These are made of pure semiconductor materials such as silicon or germanium. Electrons get excited from valance band to conduction band when photons of enough energy fall on it and the number charge carriers are increased.
- Extrinsic photoresistors: These are semiconductor materials doped with impurities which are called dopants. These dopants create new energy bands above the valence band which is filled with electrons. Hence this reduces the bandgap and less energy is required in exciting them. Extrinsic photo resistors are generally used for long wavelengths.
Construction of a Photocell
The structure of a light-dependent resistor consists of a light-sensitive material which is deposited on an insulating substrate such as ceramic. The material is deposited in a zigzag pattern in order to obtain the desired resistance and power rating. This zigzag area separates the metal deposited areas into two regions.

Then the ohmic contacts are made on either sides of the area. The resistances of these contracts should be as less as possible to make sure that the resistance mainly changes due to the effect of light only. Materials normally used are cadmium sulfide, cadmium selenide, indium antimonide, and cadmium sulfide. The use of lead and cadmium is avoided as they are harmful to the environment.
Applications of Photoresistors (LDRs)
Photoresistors (LDRs) have low cost and simple structure and are often used as light sensors. Other applications of photoresistors include:
- Detect absences or presences of light like in a camera light meter.
- Used in street lightning designs (can be combined with a good arduino starter kit to act as a street light controller)
- Alarm clocks
- Burglar alarm circuits
- Light intensity meters
- Used as part of a SCADA system to perform functions such as counting the number of packages on a moving conveyor belt








No comments: